Every day, we encounter remarkable advancements brought about by technology. These advancements enhance our lives. Even so, our digital-enhanced world is riddled with risks because of the increased complexities that technology brings.
A good example of the risks that the world faces today because of technology is the way hackers disrupt day-to-day normal operations. They seek vulnerabilities in technological infrastructures, causing disruptions in corporate, commercial, or government operations. At times, their goal is to gain financially from their actions.
Given the constant threat caused by shifting technological evolution, it’s important to have a robust cyber security management system for all kinds of organizations. This emphasizes the need for decision-makers in civil society, academia, industry, and government to anticipate and address current and future cybersecurity challenges to stay ahead.
According to Gartner Senior Director Analyst Richard Addiscott, “The renewed focus on the human element continues to grow among this year’s top cybersecurity trends. Security and risk management leaders must rethink their balance of investments across technology, structural and human-centric elements as they design and implement their cybersecurity programs.”
From the challenges of maintaining adequate levels of staffing and obtaining insurance, to increasing adoption of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) to bolster cyber security, this article aims to highlight key trends that will continue to shape the cyber security market in 2023 and beyond.
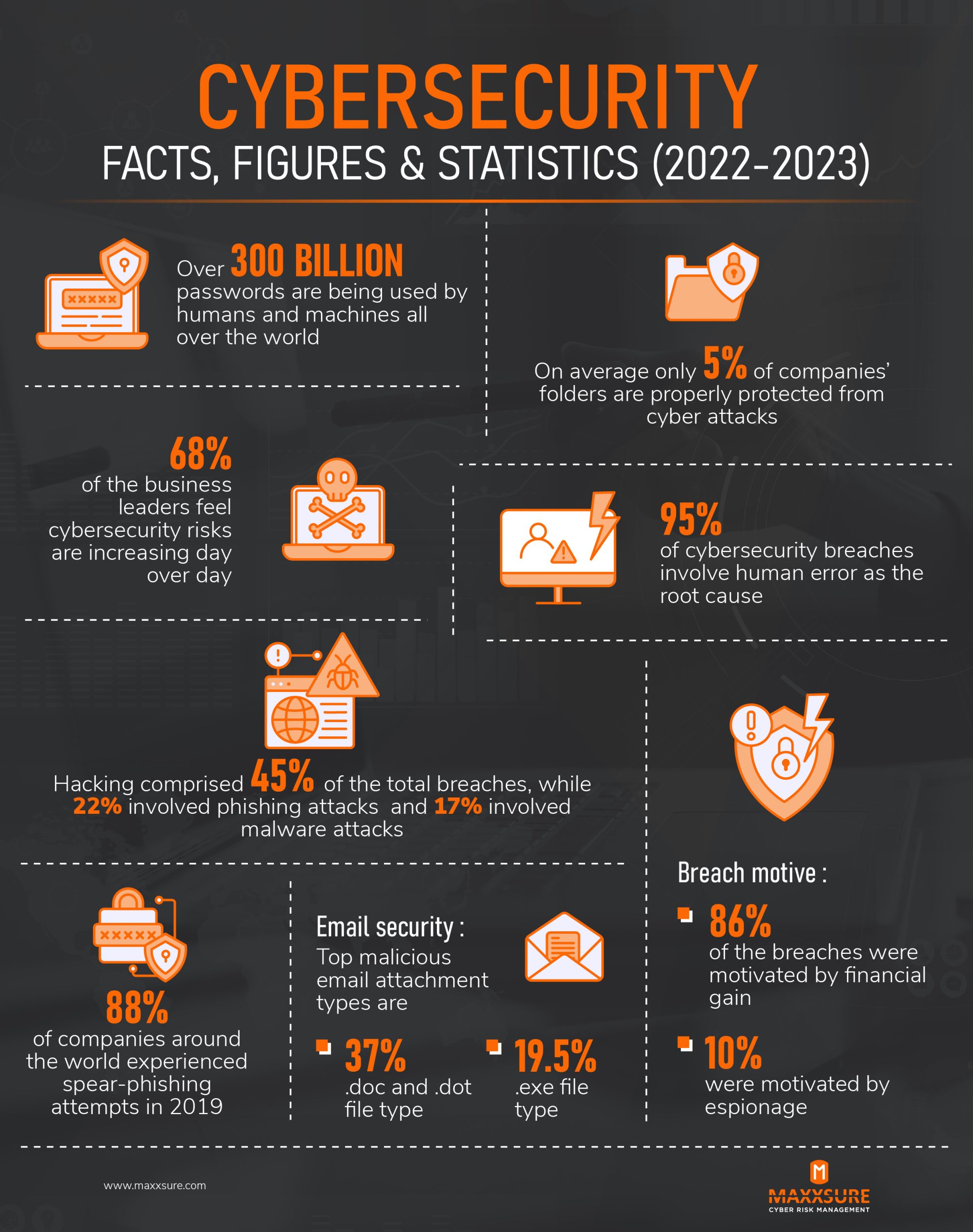
Cybersecurity Facts, Figures, and Statistics 2022-2023
Cyber-crime is growing exponentially. According to Xyno Consulting’s partner and cyber risk management expert, Maxxsure, breaches in cybersecurity are motivated by financial gain or espionage. Considering over 300 billion passwords are being used by humans and machines worldwide, breaches are getting more aggressive.
Before we can understand the complexities of cyber risks and urgency of cybersecurity resiliency, we need to understand at least the basic facts about it. Here are the other facts, figures and statistics about cybersecurity in 2023.
- 88% of companies around the world experienced spear-phishing attempts in 2019 alone
- Hacking comprised 45% of the total breaches, while 22% involved phishing attacks and 17% involved malware attacks
- 95% of cybersecurity breaches involve human error as the root cause
- 68% of business leaders feel cybersecurity risks are increasing day over day
- On average, only 5% of companies’ folders are properly protected from cyber attacks
- In email security, 37% of malicious attachment types are .doc and .dot, while 19.5% are .exe file type.
Top 7 Cybersecurity Threats to Prepare for in 2023

The risk of cyber attacks will increase as organizations continue to take the digital plunge. It’s important therefore, for organizations to keep up with top cybersecurity threats. It should be part of their business plan. Staying in the know about the latest dangers can help them protect themselves, their customers, and both their reputations.
The cybersecurity landscape, however, will continue to evolve. Threats will differ every year and as the world navigates the last quarter of 2023, here are the biggest cyber threats to watch out for.
1. Human errors
According to Maxxsure, 95% of cybersecurity breaches involve human error as the root cause. The key solution here is for organizations to take technical considerations into account, especially across the life cycle of providing controls management to employees. Employee experience is important, but effective people and talent management should be practiced to encourage functional and technical maturity.
2. Employees working remotely
On average, only 5% of companies’ folders are properly protected from cyber attacks. When employees work remotely, there’s little protection that organizations will have against cyber attacks of corporate files are not protected. To solve this problem, organizations should:
- Consider all devices and connections as unsecure before allowing access to them.
- Not allow employees to share passwords. Only strong passwords should be used.
- Prohibit employees from connecting through public Wi-Fi. Instead, provide secure VPN connections for them.
3. Critical infrastructure attacks
In recent years, we’ve seen attacks on critical infrastructure such as the 2017 NotPetya attack that crippled the global shipping industry and the 2021 Colonial Pipeline system hacking that led to its shutdown.
Experts say that to help protect infrastructure, strengthening the American Cybersecurity Act will help immensely. It will require critical infrastructure entities to report cyber incidents within 72 hours, and ransomware payments within 24 hours, to CISA (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency).
4. Mobile-first attacks
Nearly every single person in the world owns a mobile phone. Majority of users are adults who are employed. While they use their phone for personal reasons, they also use it to communicate with their co-workers, open emails, and other work-related activities. And just like computers and laptops, mobile phones are susceptible to cyber attacks such as phishing, malicious apps, spyware, and poor password security.
5. Cloud breaches
Cloud services are vulnerable to cyber attacks. As more organizations shift to cloud delivery models, cloud breaches will increase. In fact, 27% of organizations reported cloud breaches in the previous year alone. Cyber attacks on cloud services include account hijacking and Denial of Service (DoS) attacks, which prevent companies from being able to access their data.
6. Attacks on Internet of Things (IoT) devices
Like mobile phones, laptops, and computers, Internet of Things (IoT) devices are susceptible to cyber attacks because of their ability to connect to the internet. In the US, 70% of homes have at least a single smart device. This makes them more vulnerable to cyber attacks. In fact, between January and June of 2021, there were over 1.5 billion breaches in American households.
7. State-sponsored political attacks (targeting government assets)
In a 2019 report by Thomson Reuters Labs, it was revealed that 22 countries are suspected of sponsoring cyber operations, including the US.
Cyber attacks not only happen on private individuals and corporate organizations. Governments are also under attack. It may sound ominous, but it still happens. Entire governments are infiltrating other governments with their cyber skills. When infiltrated, attacks on critical infrastructure are performed.
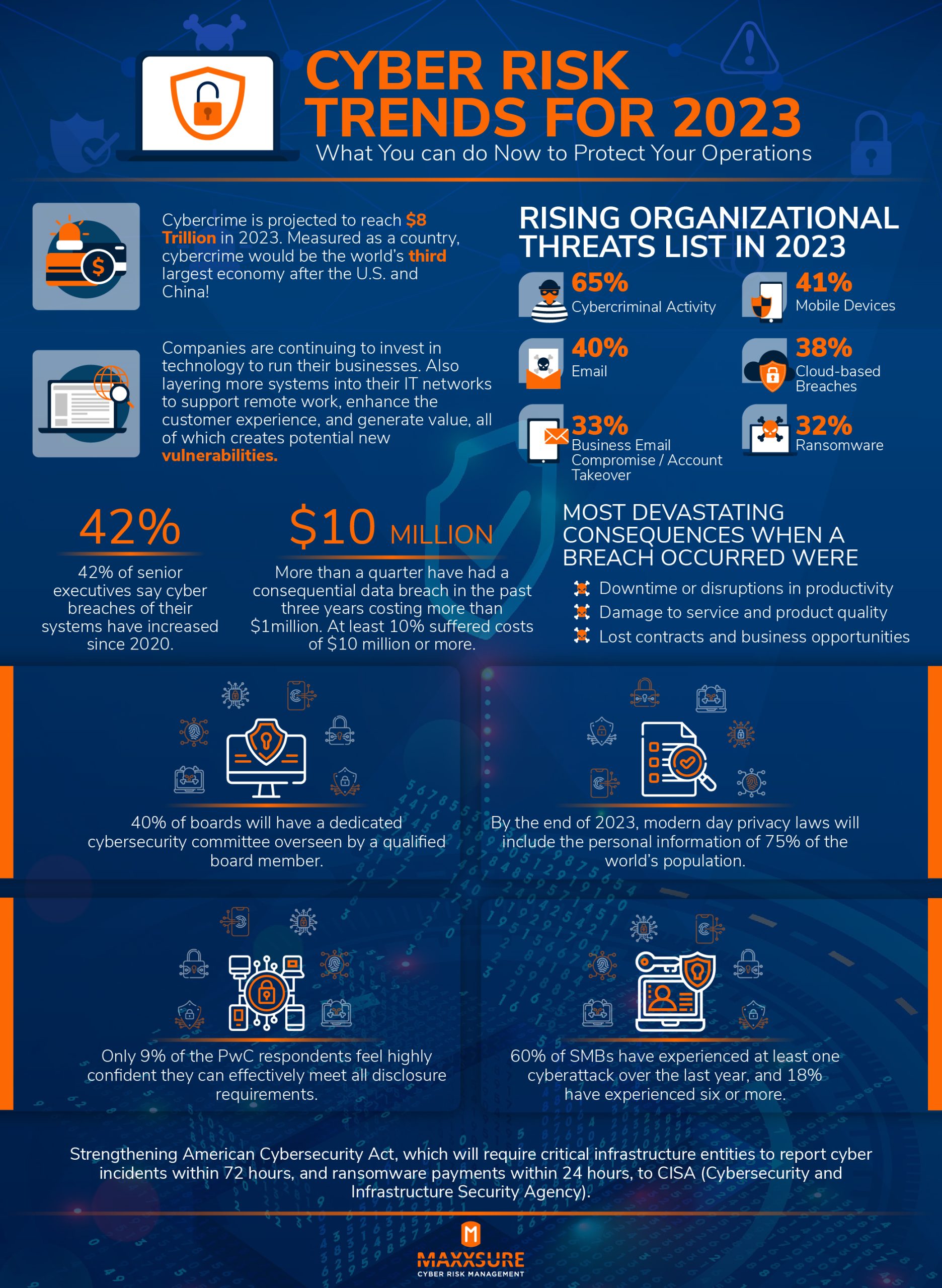
Cyber Risk Trends for 2023
According to Maxxsure, companies are continuing to invest in technology to run their businesses. They are layering more systems into their IT networks to support remote work, enhance the customer experience, and generate value. However, all of these creates potential new vulnerabilities in their systems as well. Considering this, here are cyber risk trends to watch out for until the year ends.
- Cybercrime is projected to reach $8 trillion in 2023. Measured as a country, cybercrime would be the world’s third largest economy after the US and China.
- 42% of senior executives say cyber breaches of their systems have increased since 2020.
- $10 million. More than a quarter have had a consequential data breach in the past three years costing more than $1 million. At least 10% suffered costs of $10 million or more.
- The rising organizational threats list in 2023 include: 65% cybercriminal activity, 40% email, 33% business email compromise/account takeover, 41% mobile devices, 38% cloud-based breaches, and 32% ransomware.
- 40% of boards will have a dedicated cybersecurity committee overseen by a qualified board member.
- By the end of 2023, modern day privacy laws will include personal information of 75% of the world’s population.
- Only 9% of the PwC respondents feel highly confident they can effectively meet all disclosure requirements.
- 60% of SMBs have experienced at least one cyberattack over the last year, and 18% have experienced six or more.
Looking Forward – A Conclusion
Millions of hackers are working around the clock to develop strategies for their next attack. It happens more quickly than organizations can update their defenses. The sad truth is that even the most well-fortified cybersecurity system can’t protect organizations against attacks.
The most devastating consequences when a cyber attack occurs are downtime or disruptions in productivity, damage to service and product quality, and unfortunately, lost contracts and business opportunities. Organizations therefore, must adopt a proactive approach to fight cyber attacks and manage cyber risks.
References:
https://www.gartner.com/en/articles/top-strategic-cybersecurity-trends-for-2023
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2023/03/trends-for-future-of-cybersecurity/
https://www.financierworldwide.com/cyber-security-trends-in-2023-and-beyond
https://www.thomsonreuters.com/en-us/posts/news-and-media/state-sponsored-cyberattacks/




